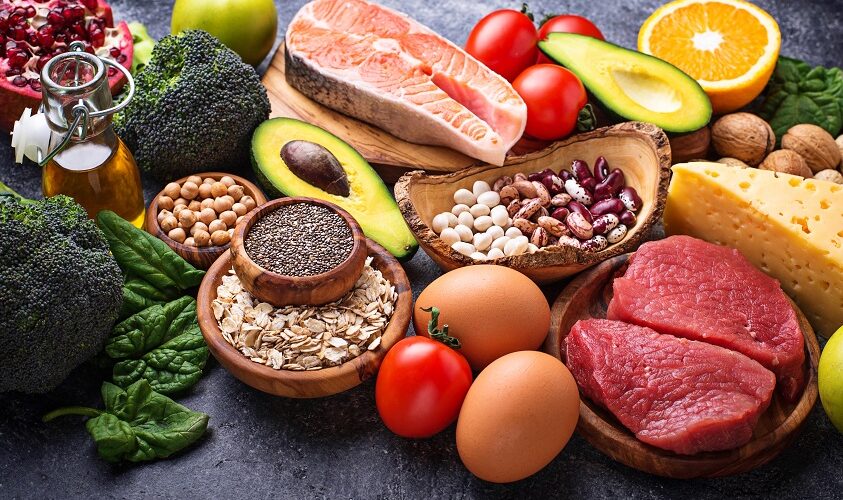
Nutrition is one of the most important factors for the general health and well-being. Healthy eating habits and a balanced diet are essential for maintaining a healthy body, mind, and spirit. This guide discusses the importance of nutrition, types of nutrition, benefits of nutrition, how to maintain a healthy diet, and top nutrition tips. Keep reading to know more about nutrition in simple terms with this detailed guide.
Word to the Wiser assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or omissions in the content of this site. The information contained in this site is provided on an “as is” basis with no guarantees of completeness, accuracy, usefulness or timeliness.
What You Should Know About Nutrition Basics
Nutrition is one of the most confusing topics for modern working adults. Healthy eating habits are essential to living a long, happy life. However, with so much information coming from so many different places and people, it can be challenging to stay informed about what is healthy and what isn’t. If you work in a fast-paced office and don’t have time to research everything online, this section will give you a crash course in nutrition basics and some advice on how to make healthy eating choices every day.
What Are The Basics Of Nutrition?
Nutrition is the science of eating right. It’s the study of macronutrients and micronutrients, nutritional needs, dietary patterns, food preparation, and all other factors that lead to health through food. The basics of nutrition include:
- Macronutrients: Protein, carbohydrates, and fat are the macronutrients we consume daily. They provide the calories (energy) needed for essential bodily processes and the building of new tissue. The recommended dietary intake (RDI) for macronutrients is based on gender, age, activity level, and health status.
- Micronutrients: Vitamins and minerals are the micronutrients we get from food. They help us grow, heal, and stay healthy. A healthy daily dietary intake of micronutrients is essential to maintain good health.
How Many Calories Do We Need?
Calories are units of energy found in the foods we eat. We need calories to survive, but too many can lead to weight gain and obesity. To calculate how many calories your body needs, multiply your current weight by 12-14. For example, if you weigh 150 lbs, you need about 2,300 calories per day. This is the amount of energy your body uses each day to stay alive. If you want to lose some weight, you can either decrease the amount of food you eat or increase your daily physical activity.
Protein, Carbohydrates and Fat – What’s Which?
- Protein – This is the macronutrient you should eat the most. It is an essential nutrient that helps build and repair your muscles, bones, and skin. It also helps your body make hormones necessary for growth and development. You can get protein from meat, fish, eggs, dairy, beans, soybeans, and other legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Carbohydrates – These are found in grains, fruits, and vegetables. They provide energy for your brain, nervous system, and muscles. If you choose to follow a low-carb diet, remember that you still need to eat enough protein to stay healthy.
- Fat – This is necessary for the absorption of certain vitamins and minerals. But too much dietary fat can lead to heart disease and weight gain. You should try to avoid saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
Get The Right Mix of Nutrients
To keep your health in check and avoid diseases, your daily diet should include vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that your body needs. There are two main dietary patterns: The Western Diet and the Mediterranean Diet.
- Western Diet – This is the typical diet in the US and other developed countries. It’s high in fat and sugar from processed foods, red meat, and dairy products.
- Mediterranean Diet – This pattern is based on a diet linked to lower rates of heart disease, cancer, and other diseases common to the West. It emphasizes eating lots of vegetables and fruits, nuts, beans, whole grains, fish, and olive oil as the main source of dietary fat.
Food Groups to Focus on
The best way to eat a healthy diet is to choose foods from all five food groups. This will give you essential vitamins and minerals and help you maintain a healthy weight.
- Vegetables – Choose a variety. Beans – Eat fiber-rich legumes like beans and lentils.
- Fruits – Eat two pieces of fruit daily. Whole grains – Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Dairy – Eat low-fat dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Meat and fish – Choose lean meats low in red meat.
Bottom line
To stay healthy, you must eat a balanced diet. This means getting enough nutrients and calories through a wide variety of foods. You should also eat a variety of foods from all five food groups. The best way to eat a healthy diet is to choose foods from all five food groups.
Why Nutrition Matters
Good nutrition is essential to optimal health and longevity. It’s something that many of us take for granted and often overlook, but the reality is that nutrition has a major impact on our physical and mental well-being. Proper nutrition can help us to maintain a healthy weight, reduce our risk of chronic diseases, and even improve our mood and outlook on life. Beyond simply ensuring that we’re getting the right types of nutrients, nutrition also involves considering how our diet affects our overall health and longevity. This means considering the quantity and quality of the food we eat, as well as its impact on our bodies. In this section, we’ll explore why nutrition matters and the considerations to make when striving for optimal health and longevity.
Types of Nutrients
There are three main types of nutrients to consider when we’re talking about good nutrition: macronutrients, micronutrients, and phytonutrients. Macronutrients are nutrients our bodies need in large quantities; these include carbohydrates, protein, fiber, and fat. Micronutrients are nutrients our bodies need in smaller amounts; these include vitamins and minerals. Finally, phytonutrients are compounds found in plants that are beneficial for health; these include resveratrol in red wine and curcumin in turmeric. Phytonutrients have been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that may aid in preventing chronic diseases. It’s important to note that the composition of micronutrients and phytonutrients can vary widely depending on the type of food they’re found in. Nevertheless, these are the primary nutrients we should consider when we think about good nutrition.
Quantity and Quality of Food
As with any other aspect of life, when it comes to nutrition, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Instead, there are general guidelines we can follow to ensure that our diets are healthy. The first thing to consider is the quantity of food we’re eating. It’s important to get enough calories and nutrients to meet our body’s needs, but we also don’t want to overeat and put ourselves at risk for obesity and other health problems. For most adults, a daily calorie intake of about 2000-2500 is recommended for women and 2500-3000 for men. Beyond this, you can use a calorie calculator to determine the right daily calorie intake for you. Next, we want to consider the quality of the food we’re eating. This includes the types of food we’re eating (e.g., vegetables, fruits, grains, etc.) as well as their freshness and cleanliness. It’s important to take these factors into account to ensure that each meal is as healthy as possible.
Benefits of Good Nutrition
Beyond simply meeting our daily nutritional requirements, good nutrition can help us to maintain a healthy weight and reduce our risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. It can also help to improve our mood and outlook on life by increasing our energy levels, improving our sleep, and reducing our stress levels. Furthermore, good nutrition can even help us to live longer and reduce our risk of certain types of cancers. All of these benefits are reasons to make nutrition a top priority, but it’s important to note that not all types of diets are created equal. Some diets may provide the right amount of calories and nutrients, but others may provide too much or too little of certain nutrients, which can have negative effects on our health. For example, while it’s true that a high-fat diet can help you meet your daily calorie requirements, it’s also associated with an increased risk of heart disease and certain cancers.
Impact of Diet on Health and Longevity
Beyond the immediate benefits of good nutrition, there’s also evidence that a healthy diet can help us to extend our lifespan. This is largely due to the fact that certain types of diets can reduce our risk of chronic diseases, which are a leading cause of death among adults. For example, a healthy diet high in fruits and vegetables can help to reduce our risk of certain types of cancers, which can reduce our risk of death by as much as 25%. Although there are many studies that show the benefits of a healthy diet, there are also some studies that show that it might not be enough to achieve optimal health and longevity. This is because there are two other important factors that nutrition can’t control: how often we eat and how much we exercise. For optimal health and longevity, it’s important to eat enough calories, but not too many, as well as to exercise regularly.
Considerations for Optimal Health and Longevity
Beyond the quantity and quality of the food we eat, there are also other aspects of our diets that are important for achieving optimal health and longevity. The first is our meal frequency, i.e. how often we eat each day. There are two main schools of thought on this: one where we eat three times per day, and one where we eat six times per day. There are merits to both approaches, but most studies show that eating three times per day is the best approach for achieving optimal health and longevity. The second consideration is sleep, as research shows that getting enough sleep may be just as important as eating a healthy diet. Finally, hydration levels are also important, as we need to drink enough water each day to stay hydrated. Beyond these considerations, there’s also evidence to suggest that certain supplements may help to improve health and longevity. These include vitamin B12, fish oil, folic acid, and multivitamins.
Strategies for Achieving Good Nutrition
Now that we know why good nutrition matters and the considerations to make when striving for optimal health and longevity, we can discuss strategies for achieving good nutrition. The first thing to do is to make sure you’re meeting your daily nutritional requirements. This can be done by consulting a daily diet plan or finding a nutritional website that recommends daily meal plans. Next, make sure to eat the right types of foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and proteins. Finally, don’t forget about hydration, as it’s easy to get distracted by other aspects of our lives and forget to drink enough water.
Fruits and Vegetables You Should Be Eating More Of
Eating more fruits and vegetables is a great way to improve your diet and stay healthy. These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that are beneficial for our health. Research has shown that eating more fruits and vegetables can help reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer. There are so many different types of fruits and vegetables out there, that it can be hard to keep track of them all! This section lists the top fruits and veggies you should be eating more of. With these nutrition powerhouses in your diet regularly, you’ll feel great and look even better.
Beans and Legumes
Beans and legumes are excellent sources of plant-based protein, fiber, and minerals. They are also relatively inexpensive and can be eaten in many different ways—soaking, sprouting, or roasting them may be required for some types. Beans and legumes can be enjoyed as a side dish, added to stews and casseroles, or eaten in place of meat in vegetarian meals. The best types of beans and legumes are black beans, pinto beans, navy beans, kidney beans, chickpeas (garbanzo beans), lentils, and soybeans. To meet your daily fiber needs, aim to eat 2 cups of beans or legumes each week.
Dark Leafy Greens
Dark leafy greens are nutritional powerhouses, full of vitamins and minerals. These include calcium, iron, magnesium, and vitamins A, C, and K. Some types of dark leafy greens include arugula, broccoli, bok choy, collard greens, endive, kale, and Swiss chard. Dark leafy greens can be eaten as a side dish, added to salads, or even juiced. To meet your daily fiber needs, aim to eat 2 cups of dark leafy greens each week.
Fruits
Fruits are packed with vitamins and minerals but contain very little fat and almost no cholesterol. Some of the best fruits to eat include apples, apricots, bananas, blueberries, cantaloupe, grapefruit, oranges, strawberries, and watermelon. You can eat most fruits as snacks or as additions to meals, like on top of cereal or oatmeal. To meet your daily fruit needs, aim to eat 2 cups of fruit each week.
Whole Grains
Whole grains are rich in fiber and contain many vitamins and minerals. Some of the best whole grains are oats, quinoa, whole wheat, barley, and brown rice. Whole grains can be eaten in many different ways, including in baked goods, as side dishes, and in salads. To meet your daily fiber needs, aim to eat 2 cups of whole grains each week.
Bottom line
Fruits and vegetables are essential for a healthy diet. Eating more of them can help reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases like heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes, as well as some types of cancer. There are many different types of fruits and vegetables out there, so it can be hard to keep track of them all! This section lists the top fruits and vegetables you should be eating more of. With these nutrition powerhouses in your diet regularly, you’ll feel great and look even better.
How to Eat for a Calorie Deficit
Let’s say you want to lose weight. Or, let’s say that your doctor has told you that you need to lose some weight and has given you a specific target. That target is the number of calories you need to eat per day to achieve your goal. If you have ever been on any kind of diet, whether that’s cutting carbs or fat or anything else, then you know that calculating how many calories are in what you eat plays an important role. This is one of the primary mechanisms by which most diets work — either they reduce the number of calories that we eat, or they help us avoid eating so many calories through various tricks and techniques.
What is a Calorie Deficit and How Does it Help Me Lose Weight?
A calorie deficit is simply the act of eating fewer calories than you burn. If you eat 500 fewer calories than you burn, you are in a deficit of 500 calories per day. If you maintain that deficit long enough, you will lose weight. Of course, there is more to it than that. The reason that most of us even care about calorie intake is that, in large part, it determines how much weight we lose and where that weight comes from. If we eat a surplus of calories — if we eat more than we burn — we store those extra calories as fat. If we eat less than we burn, we will lose fat.
A Calorie is a Unit of Energy
A calorie is nothing more than a unit of energy. It is how much energy we get from consuming food. And when we talk about how many calories you need to eat to lose weight, we are not concerned with how tasty or satisfying the food is. The only thing that matters is how many calories are in each food item. When we are counting calories, we are simply trying to get as close as we can to our “calorie requirement”. Your calorie requirement (or daily calorie goal) is the number of calories that you need to eat each day to achieve your goal. And while this may seem tedious, counting calories and calculating your calorie requirements can be quite easy.
Why Should I Care About How Many Calories I Eat?
When it comes to dieting and weight loss, calories are king. The number of calories that we eat will determine whether we lose fat or gain fat. And the more we know about calories, the easier it will be for us to achieve our goals. If we are trying to lose weight, then we need to eat fewer calories than we burn. And if we are trying to gain weight, we need to eat more calories than we burn. There is no single factor that determines how quickly we will lose weight. Factors like genetics, activity level and metabolism will all play a role. But when it comes to the sheer mechanics of losing weight, the one thing that always holds is that we must eat less than we burn.
Tips for Eating in a Calorie Deficit
If you are eating a calorie deficit, the first thing that you need to do is calculate your daily calorie goal. – First, determine your BMR. – Then, add an activity factor. – Chart your calories. If you are not eating enough calories, then you will probably lose weight. However, if you are not eating enough calories, then you are likely to make poor progress in the gym and you will probably feel lousy as well. If you are eating too many calories, then you will not lose weight. You may even gain weight. But if you are eating too many calories, then you will probably feel pretty good and you will probably make good progress in the gym.
Bottom line
If you are trying to lose weight, then you need to eat fewer calories than you burn. If you want to lose 10 pounds in 3 months, then you need to eat about 3,500 fewer calories than you burn each month. Keep in mind that these are just averages and that your results will depend on your genetics and your activity level. If you want to lose fat and not muscle, then you want to eat at a calorie deficit that is sustainable for you. And, if you follow these tips, you will be able to do just that! In the end, there are no shortcuts when it comes to weight loss. You will have to put in the work. But if you are smart about it, then it will be a lot easier and it will take less time.
Diabetic Diet: Tips and Recipes for a Healthy Life
Having diabetes doesn’t mean that you have to give up on the foods you love. There is a diet and lifestyle changes that can help manage your condition so that it doesn’t become a debilitating illness. The key is to balance your carbs, fats, and proteins while also reducing sugars where possible. This article will help you understand what a diabetic diet means. It covers everything from the general principles of a healthy diet to specific examples of meal plans. You won’t need to go hungry or feel like you are eating cardboard again!
What does a diabetic diet include?
The best way to start looking at the diabetic diet is to look at what foods you need to limit or avoid. You can then work out how to incorporate other foods into your diet in a way that is healthy for you. All carbohydrates – including starches, sugars and fiber – are broken down into sugar during digestion. For healthy people, this is not an issue because insulin is secreted to help regulate the amount of sugar in the bloodstream. However, for people with diabetes, this doesn’t always happen properly. This is why a diabetic diet focuses on reducing carbs. Vegetables and fruits – These are excellent additions to any diet. They contain fiber, vitamins and minerals. All of these things are important for maintaining good health. Fats and proteins – If you reduce your carb intake, you also need to increase your protein and fat intake. This will help you feel full and maintain muscle mass while keeping blood sugar under control.
Carbs: Good and bad
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body. They are broken down into glucose, which is used by the body for energy. Carbohydrates are found in foods like rice, pasta, bread and potatoes. A diabetic diet means reducing your intake of carbohydrates because they are broken down into glucose and can alter your blood sugar levels. There are two types of carbohydrates in food:
Simple carbohydrates: This is the type of carbohydrate that should be avoided in a diabetic diet. They include foods like sugary soft drinks, candies, and all types of sugary baked goods.
Complex carbohydrates: This is the type of carbohydrate that you should be eating more of. They include foods like grains (like rice, quinoa, and oats), root vegetables (like carrots, beets and sweet potatoes), legumes (like beans, peas, and lentils), and dairy products.
Bottom line
A diabetic diet is designed to help blood sugar levels stay as normal as possible. It focuses on eating plenty of vegetables and fruits – which are low-carb, high-nutrient foods – as well as proteins and fats to help maintain muscle mass. While there is no “one size fits all” diet plan, there are some general dietary principles that can help you better manage your diabetes. They include: – Eating more vegetables and fruits (and less candy and processed foods). – Eating more whole grains, legumes and nuts. – Eating smaller, more frequent meals and snacks. – Reducing your intake of sugar.